Oui mais je dois faire le ménage et il faut aussi que je mette un debonce sur l’interrupteur de sens, ce sera plus propre.
Le voila donc en l’état, il fonctionne mais il sera amélioré.
Le premier potar doit être branché sur A0, le second A1 etc…
La bibliothèque nécessaire est téléchargeable ici GitHub - pierremolinaro/acan2515: MCP2515 CAN Controller Driver for Arduino
ou mieux, avec l’IDE Arduino outils → gerer les bibliothèques → rechercher ACAN2515
#include <ACAN2515.h>
//——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
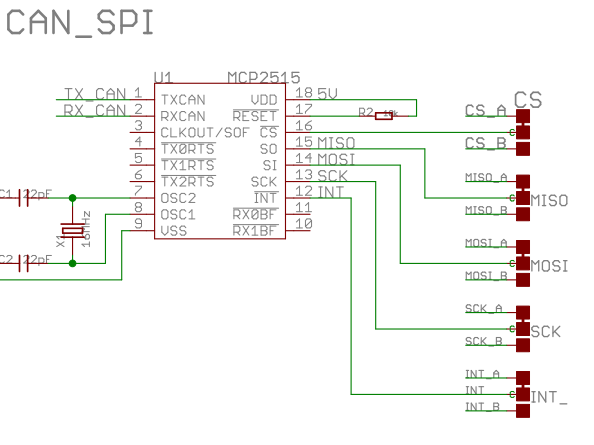
// MCP2515 connections:
// - standard SPI pins for SCK, MOSI and MISO
// - a digital output for CS
// - interrupt input pin for INT
//——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
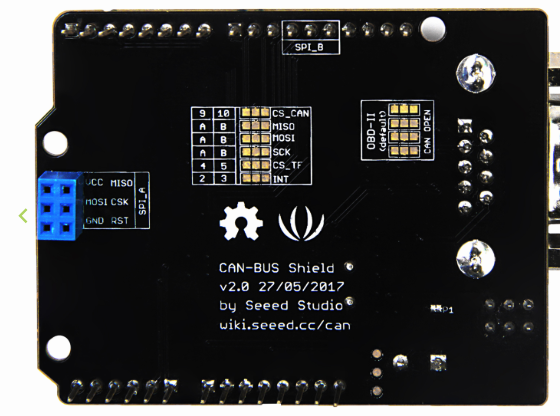
// If you use CAN-BUS shield (http://wiki.seeedstudio.com/CAN-BUS_Shield_V2.0/) with Arduino Uno,
// use B connections for MISO, MOSI, SCK, #9 or #10 for CS (as you want),
// #2 or #3 for INT (as you want).
//——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
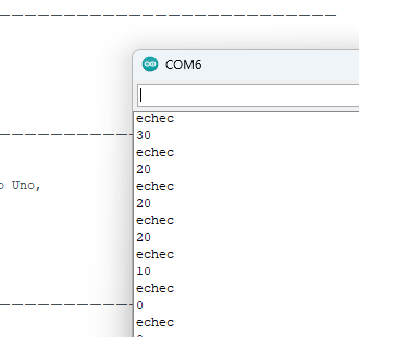
// Error codes and possible causes:
// In case you see "Configuration error 0x1", the Arduino doesn't communicate
// with the 2515. You will get this error if there is no CAN shield or if
// the CS pin is incorrect.
// In case you see success up to "Sent: 17" and from then on "Send failure":
// There is a problem with the interrupt. Check if correct pin is configured
//——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
/************************ ACAN *****************************/
// If you use CAN-BUS shield (http://wiki.seeedstudio.com/CAN-BUS_Shield_V2.0/) with Arduino Uno,
// use B connections for MISO, MOSI, SCK, #9 or #10 for CS (as you want),
// #2 or #3 for INT (as you want).
#include <ACAN2515.h>
static const byte MCP2515_CS = 10; // CS input of MCP2515 (adapt to your design)
static const byte MCP2515_INT = 2; // INT output of MCP2515 (adapt to your design)
//——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
// MCP2515 Driver object
//——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
ACAN2515 can(MCP2515_CS, SPI, MCP2515_INT);
//——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
// MCP2515 Quartz: adapt to your design
//——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
static const uint32_t QUARTZ_FREQUENCY = 16UL * 1000UL * 1000UL; // 16 MHz
class Loco {
private:
uint16_t m_address;
uint16_t m_speed;
uint16_t m_oldSpeed;
byte m_direction;
byte m_oldDirection;
byte m_speedPin;
byte m_dirPin;
public:
uint16_t speed() {
m_speed = analogRead(this->m_speedPin);
m_speed = map(m_speed, 0, 1023, 0, 100);
m_speed *= 10;
return m_speed;
}
void speed(uint16_t o) {
m_speed = o;
}
uint16_t oldSpeed() {
return m_oldSpeed;
}
void oldSpeed(uint16_t os) {
m_oldSpeed = os;
}
byte direction() {
if (digitalRead(m_dirPin)) {
m_direction = 1; // Avant
//Serial.println(m_direction);
return 1;
} else {
m_direction = 2; // Arrière
//Serial.println(m_direction);
return 2;
}
// Serial.println(m_direction);
// return m_direction;
}
void direction(byte d) {
m_direction = d;
}
void oldDirection(byte od) {
m_oldDirection = od;
}
byte oldDirection() {
return m_oldDirection;
}
void speedPin(byte ap) {
m_speedPin = ap;
}
byte speedPin() {
return m_speedPin;
}
void dirdPin(byte dp) {
m_dirPin = dp;
}
byte dirdPin() {
return m_dirPin;
}
void address(uint16_t ad) {
m_address = ad;
}
uint16_t address() {
return m_address;
}
};
const uint8_t NB_LOCO = 6;
Loco loco[NB_LOCO];
uint16_t t_address[NB_LOCO] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
byte t_speedPin[NB_LOCO] = { A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5 };
byte t_dirPin[NB_LOCO] = { 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };
//——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
// SETUP
//——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
void setup() {
;
//--- Start serial
Serial.begin(115200);
//--- Wait for serial (blink led at 10 Hz during waiting)
while (!Serial)
delay(50);
//--- Begin SPI
SPI.begin();
//--- Configure ACAN2515
Serial.println("Configure ACAN2515");
ACAN2515Settings settings(QUARTZ_FREQUENCY, 250UL * 1000UL); // CAN bit rate 250 kb/s
//settings.mRequestedMode = ACAN2515Settings::LoopBackMode ; // Select loopback mode
const uint16_t errorCode = can.begin(settings, [] {
can.isr();
});
if (errorCode == 0) {
Serial.print("Bit Rate prescaler: ");
Serial.println(settings.mBitRatePrescaler);
Serial.print("Propagation Segment: ");
Serial.println(settings.mPropagationSegment);
Serial.print("Phase segment 1: ");
Serial.println(settings.mPhaseSegment1);
Serial.print("Phase segment 2: ");
Serial.println(settings.mPhaseSegment2);
Serial.print("SJW: ");
Serial.println(settings.mSJW);
Serial.print("Triple Sampling: ");
Serial.println(settings.mTripleSampling ? "yes" : "no");
Serial.print("Actual bit rate: ");
Serial.print(settings.actualBitRate());
Serial.println(" bit/s");
Serial.print("Exact bit rate ? ");
Serial.println(settings.exactBitRate() ? "yes" : "no");
Serial.print("Sample point: ");
Serial.print(settings.samplePointFromBitStart());
Serial.println("%");
} else {
Serial.print("Configuration error 0x");
Serial.println(errorCode, HEX);
}
for (byte i = 0; i < NB_LOCO; i++) {
loco[i].speedPin(t_speedPin[i]);
loco[i].dirdPin(t_dirPin[i]);
pinMode(loco[i].dirdPin(), INPUT_PULLUP);
loco[i].address(t_address[i]);
}
}
void loop() {
CANMessage frame;
frame.ext = 1;
frame.id &= ~0xFFFF;
frame.id |= 0x1813; // hash
for (byte i = 0; i < NB_LOCO; i++) {
frame.data[2] = (loco[i].address() & 0xFF00) >> 8;
frame.data[3] = loco[i].address() & 0x00FF;
uint16_t speed = loco[i].speed();
if (speed != loco[i].oldSpeed()) {
Serial.println(speed);
frame.id |= 0x80000; // commande vitesse
frame.len = 6;
frame.data[4] = (speed & 0xFF00) >> 8;
frame.data[5] = speed & 0x00FF;
if (can.tryToSend(frame))
Serial.println("sent");
else
Serial.println("echec");
loco[i].oldSpeed(speed);
}
byte direction = loco[i].direction();
if (direction != loco[i].oldDirection()) {
Serial.println(direction);
frame.id |= 0xA0000; // commande direction
frame.len = 5;
frame.data[4] = direction;
if (can.tryToSend(frame))
Serial.println("sent");
else
Serial.println("echec");
loco[i].oldDirection(direction);
}
}
}
//——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————